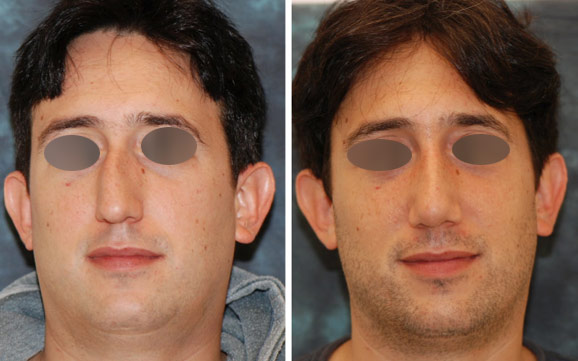
The nose is the most commonly injured facial bone. A fractured nose must be evaluated immediately for the presence of a septal hematoma (a large blot clot involving the nasal septum). If not drained promptly a septal hematoma may lead to infection, septal perforation, and long-term nasal deformity. If a perforation has developed a corrective functional rhinoplasty and septal perforation repair must be performed simultaneously to yield the best clinical outcomes.
