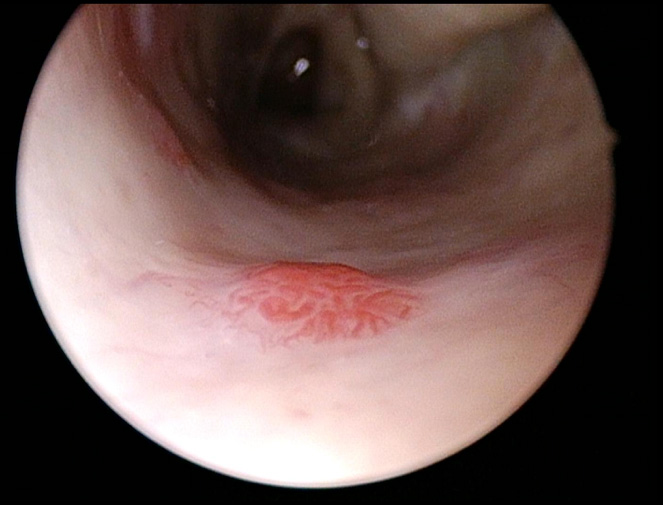
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) is a hereditary disorder characterized by abnormal clusters of weak bulging capillaries that bleed with little to no trauma or insult. They most commonly affect the nasal mucosa, but also involve the gut, skin, brain and lungs as well. Clinically patients most commonly report a history of recurrent nosebleeds (epistaxis) before being diagnosed with HHT and may suffer from lifelong recurrent epistaxis that may increase in severity as the patient ages.
